In vitro cell behavior can help elucidate drug mechanism of action, and can be a cost-effective method for testing drug efficacy. Our scientists have extensive experience many aspects of angiogenic endothelial cell behaviors.


Proliferation
Endothelial cells proliferate in response to angiogenic stimuli. We assay proliferation by incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine into DNA.
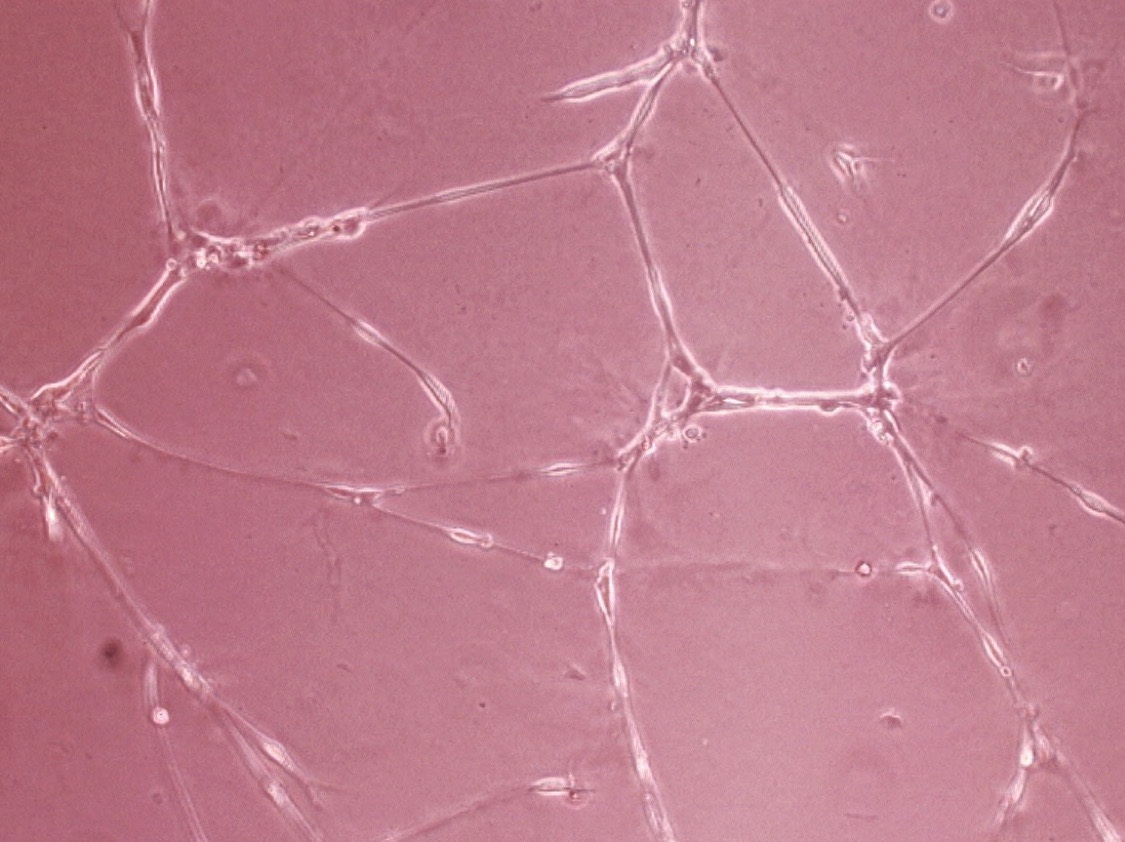
Tube formation
We assay tube formation by incubating endothelial cells on Matrigel™ and measuring and summing the lengths of connections formed between cells.
Migration
Endothelial cell migration is measured by a chemotaxis assay using a Boyden Chamber containing a membrane. Cells are seeded above the membrane and allowed to migrate towards a chemoattractant in the lower chamber. Membrane characterisitcs (pore size, pore density, etc.) can be customized to need.
Survival
Endothelial cell survival is important to maintain the health of the vasculature. We assay cell survival by a wide variety of different apoptosis assays, including incorporation of flow cytometry.
MMP Activity
Degradation of the extracellular matrix is an important precursor to angiogenesis. Cell and tissue MMP activity is measured by a variety of methods, including fluorogenic and zymographic techniques.
Permeability
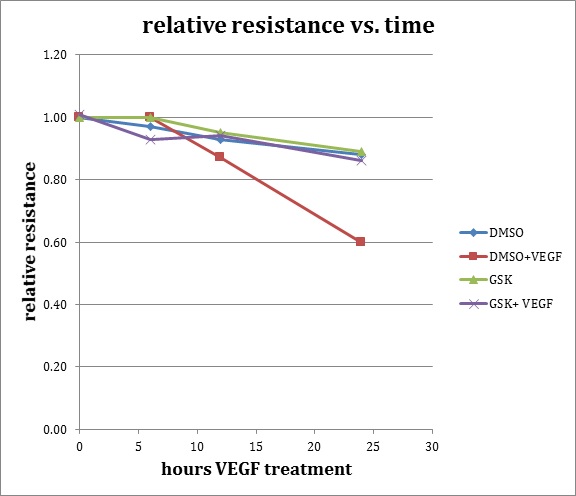
The tight junctions between retinal endothelial cells help to form the blood-retina barrier. Breakdown of this barrier results in retinal edema. To measure endothelial cell permeability, we use a trans-endothelial electrical resistance (TEER) assay.
Leukocyte adhesion
The interaction between endothelial cells and leukocytes is a main component of tissue leukostasis, an important marker of inflammation. To measure this interaction in vitro, we use a parallel plate flow chamber (PPFC) to assay leukocyte rolling over and adhesion to endothelial cells.
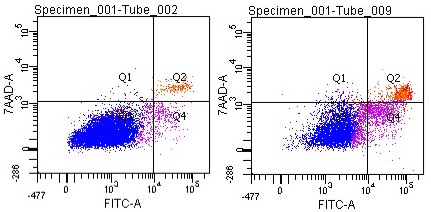
Cell Apoptosis
One of the earliest events that occurs during apoptosis (programmed cell death), is the translocation of membrane phosphatidylserine (PS) from the inside to the outside of the membrane. Annexin V, a phospholipid binding protein, has a strong affinity for PS. Labeling Annexin V with a flurochrome (ex: FITC) allows the detection of exposed PS with flow cytometry. 7AAD is a cell viability die with strong affinity for DNA, thus this die primarily labels cells undergoing later stages of apoptosis or necrosis.