| Type of Isolation | Used for Pathogens That | Equipment Needed | Use For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact | Can be spread by direct contact; often contaminate the environment | Gloves, gowns upon entering the room (Even if no patient contact is expected) | MRSA*, VRE*, scabies, C. difficile, mutlidrug resistant Gram- negative organisms, rotavirus, RSV, varicella (+ Airborne) [* if wound that is unable to be covered] |
| Droplet | Require close contact for transmission | Surgical masks | Influenza, N. meningitidis, pertussis, parvovirus |
| Airborne | Can be transmitted via airborne route | N95 respirator upon entering the room; Negative pressure room for specific pathogens | Pulmonary TB (confirmed or suspected), varicella (+ Contact), smallpox, measles |
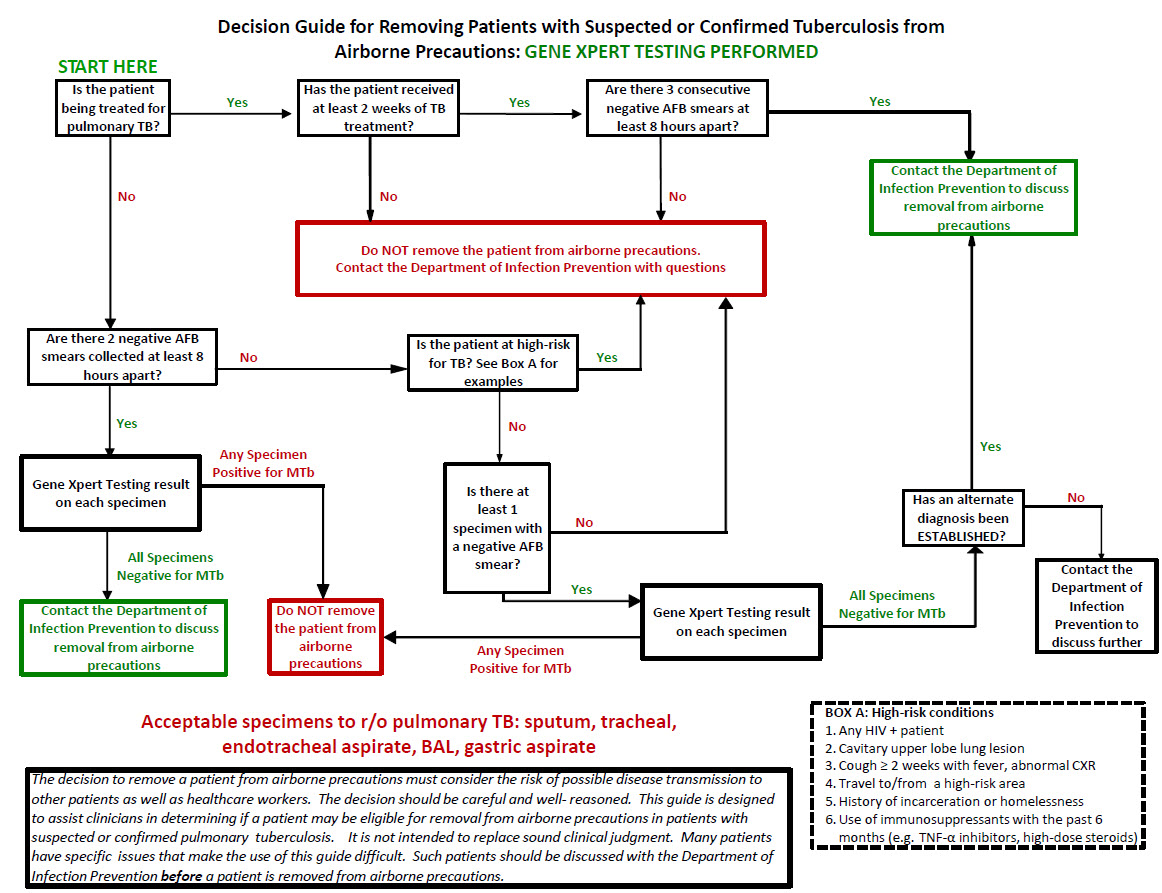
To discontinue Airborne isolation, contact Infection Prevention.
NOTE: Contact Precautions indicate that gloves and gowns are worn upon entry to the room (regardless of anticipation of contact with the patient or his or her environment).
Algorithm for removal from Airborne Precautions: download PDF
Negative Pressure Rooms
See list (HERE) - Updated June 2023
Positive Pressure Units
VUH: 11 North, 10CCT
MCJCHV: 6A, Rooms 5311 and 5312
Off campus HEPA units contact info:
Williamson county area: Shelly Wolf (615) 875-5463, Lynn Price (615) 202-8899, Located in Family Practice clinic, Medcore building.
One Hundred Oaks: Plant ops 2-2041, located in the North Box cage of OHO.
Air Exchange Information
See list (HERE)

